However, as IoT adoption scales, so do the challenges of managing connectivity efficiently. Organizations deploying large fleets of IoT devices across multiple regions must navigate logistical complexities, multiple SKUs, and the need to configure connectivity at scale. Without an efficient management system, these tasks can become resource-intensive and time-consuming.
One of the key advancements in IoT connectivity is the ability to remotely manage device subscriptions using eSIM (embedded SIM) and iSIM (integrated SIM) technologies. These technologies eliminate the need for physical SIM cards and enable seamless Remote SIM Provisioning (RSP), allowing businesses to optimize connectivity strategies and streamline operations.
To fully leverage the potential of eSIM and iSIM, IoT devices need a comprehensive management approach that includes:
- Remote SIM Provisioning (RSP): A mechanism that allows devices to switch between mobile network operators (MNOs) without physical SIM replacements.
- Bootstrap Connectivity: Initial connectivity that enables devices to communicate with a connectivity management platform (CMP) not to rely on other wireless communications before downloading an operational profile.
- A Connectivity Management Platform (CMP): A system that automates SIM provisioning and network selection based on business rules and removing the need of end user interaction.
- eIM (eSIM IoT Manager): A platform that enables businesses to gain control over the lifecycle of MNO subscriptions and manage connectivity at scale.
The SGP.32 architecture, as defined by GSMA, establishes a structured framework for enabling Remote SIM Provisioning (RSP) in IoT deployments. The following diagram illustrates how various components, including the Connectivity Management Platform (CMP) and bootstrap connectivity, interact to streamline the connectivity lifecycle. By visualizing these elements, businesses can better understand how to optimize their IoT strategies and improve device management efficiency.
Here is a simplified version of the SGP.32 architecture as defined by GSMA to allow IoT devices to take advantage of RSP (Remote SIM Provisioning) and incorporating complementary elements such as a CMP (Connectivity Management Platform) and bootstrap connectivity.
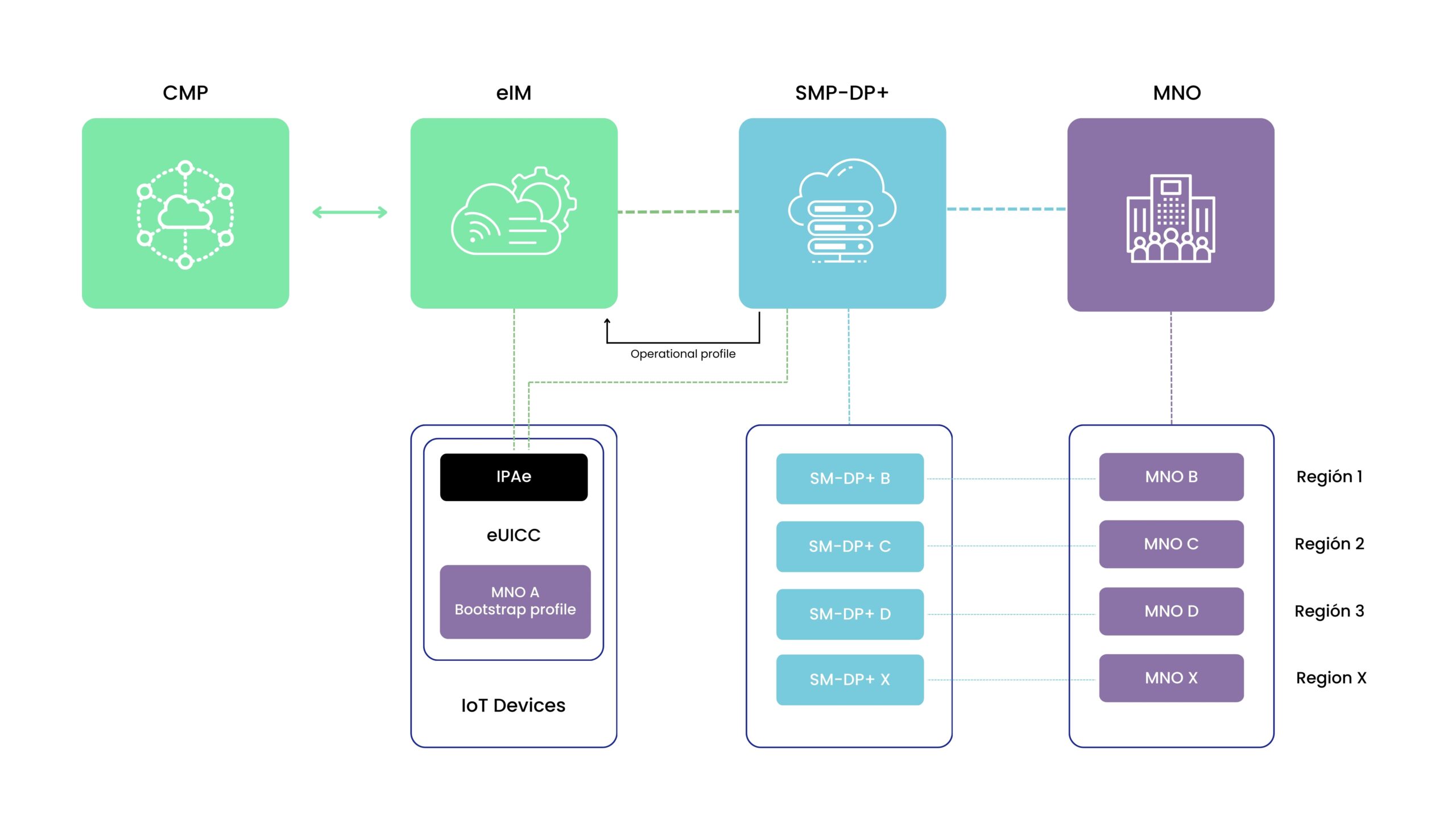
The selection of connectivity components depends on various factors, such as the type of IoT application, geographic deployment, and desired level of automation. For example, some IoT devices benefit from an IPAe (IoT Profile Assistant embedded in the eUICC) for improved integration and interoperability, while others may require IPAd (IoT Profile Assistant deployed in the device operating system), which is available for Android and Linux—the most commonly used OS for IoT devices.
By incorporating these elements, businesses can reduce logistical challenges, minimize operational costs, and enhance the scalability of their IoT deployments.
Efficient connectivity management is a critical factor in the success of IoT deployments. By adopting a strategic approach that leverages remote provisioning, automation, and streamlined connectivity management, organizations can accelerate time-to-market and optimize costs.
If you’re exploring eSIM and iSIM solutions for your IoT devices and want to learn how to manage connectivity seamlessly, our team of experts is here to help. Contact us to discuss your needs, explore solutions, and request a demo of our eSIM IoT Manager (eIM) to see how it can enhance your IoT strategy.



